Dr. Kenan Yüce
Rejuvenate, Renew, Recover with FMT!
Transform Your Gut, Transform Your Life. (FMT).

Dr. Kenan Yüce
Rejuvenate, Renew, Recover with FMT!
Transform Your Gut, Transform Your Life.
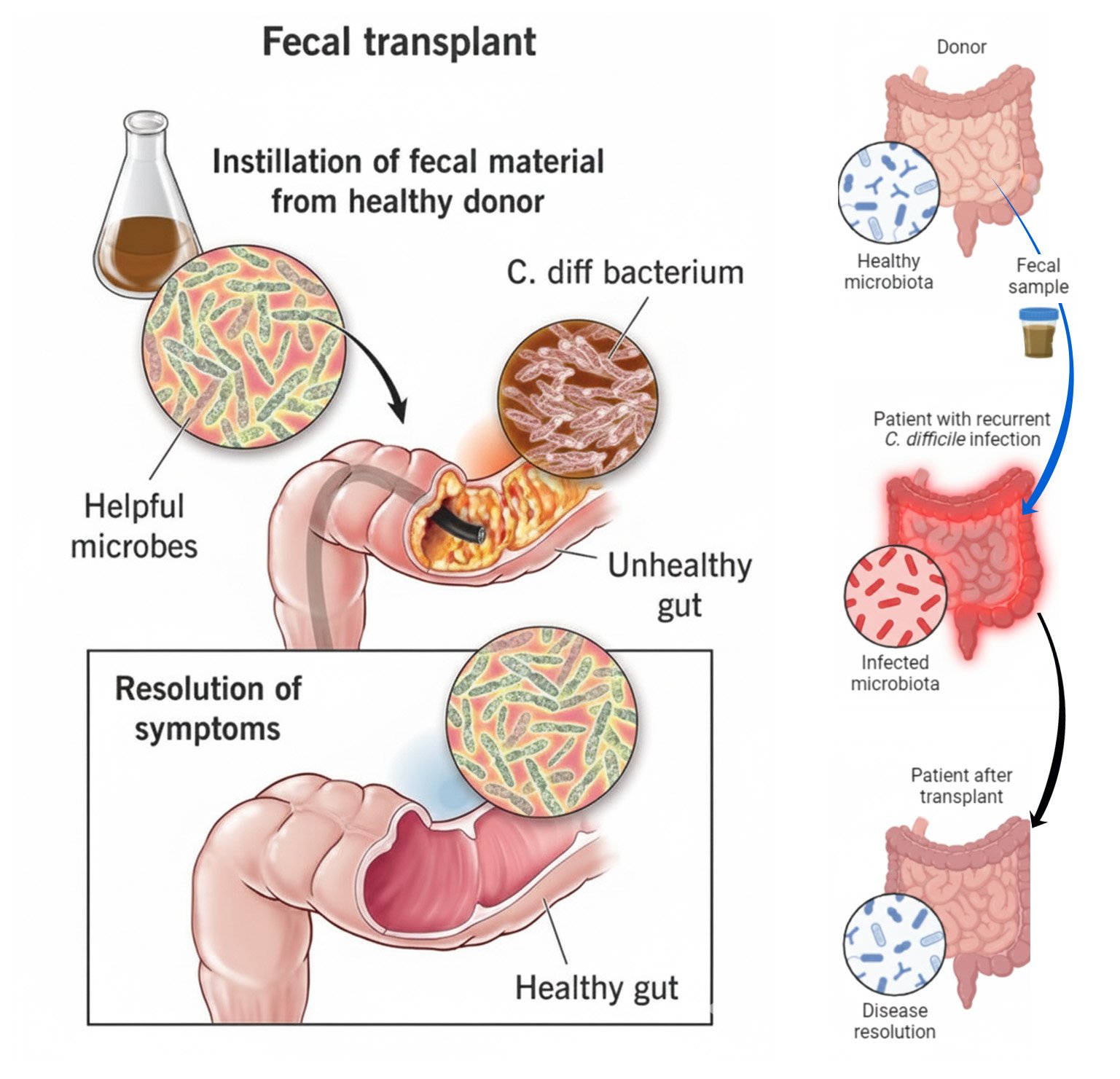
Gastrointestinal Diseases & FMT
FMT is highly effective for recurrent Clostridioides difficile infections, achieving over 90% cure rates, and is FDA-endorsed as first-line therapy. It shows promise for IBS by reducing symptoms like pain and bloating, and for SIBO by restoring microbial balance. Emerging evidence supports its role in inflammatory bowel diseases (ulcerative colitis, Crohn's), reducing inflammation and inducing remission. FMT also addresses chronic constipation by enhancing gut motility and microbiota diversity. While most effective for C. difficile, its potential for other gastrointestinal conditions is being actively researched, offering hope for patients with limited treatment options.
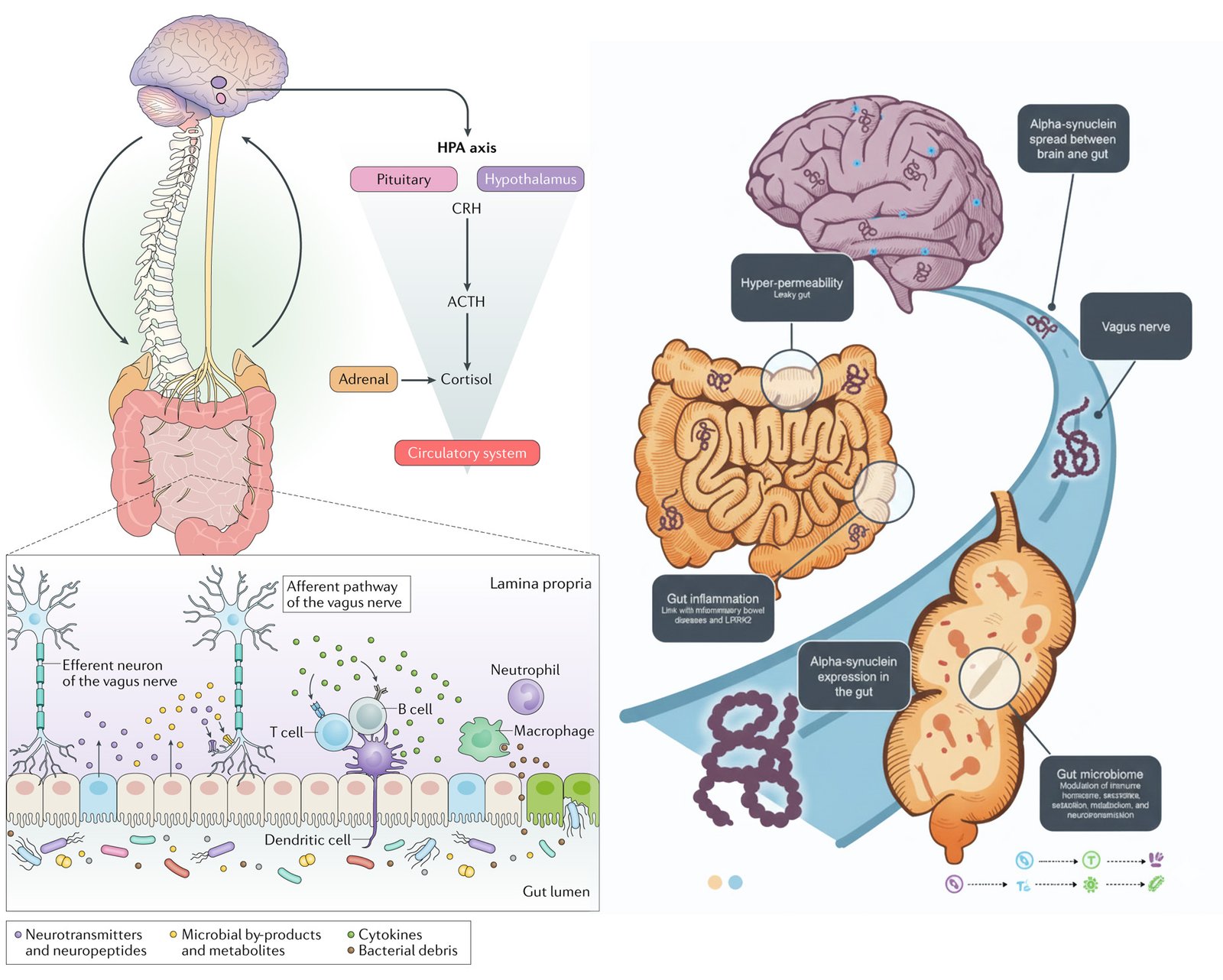
Neurologic & Neuropsychiatric Disorders & FMT
FMT is being explored for neurologic and neuropsychiatric conditions via the gut-brain axis. In autism, it has shown improvements in GI and behavioral symptoms by modulating gut microbiota. For Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, FMT may reduce neuroinflammation and amyloid plaques, though evidence is preliminary. In MS, it could help regulate immune responses and reduce neuroinflammation. For depression and anxiety, FMT targets gut dysbiosis linked to mood regulation via neurotransmitter production (e.g., serotonin). While promising, FMT for these conditions is mostly in research stages, with clinical trials underway. It represents a novel, low-risk approach for patients with limited alternatives, though long-term efficacy needs further validation.
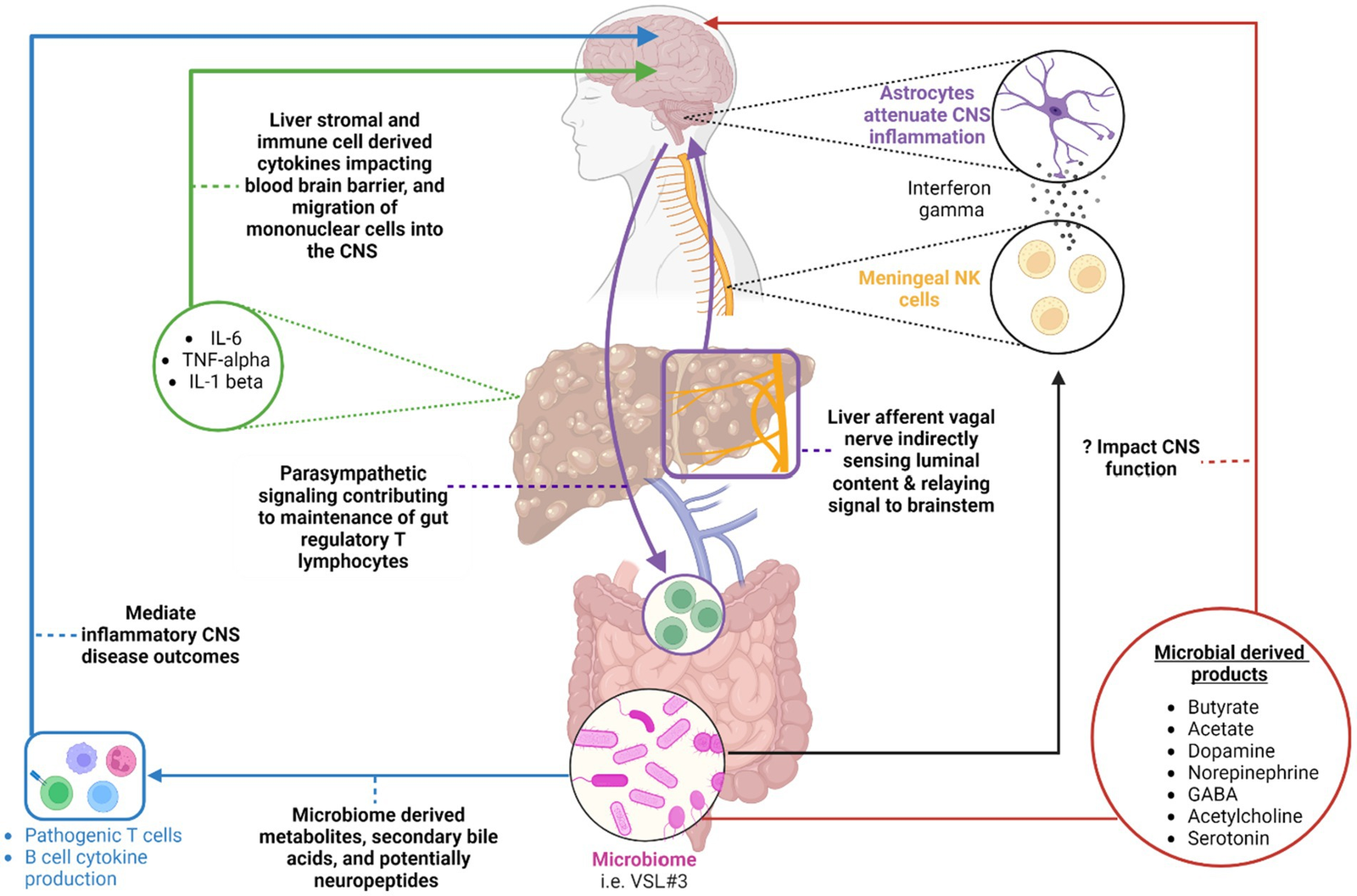
Liver Disorders & FMT
FMT shows promise for liver disorders by targeting gut-liver axis dysbiosis. In alcoholic hepatitis, FMT may reduce liver inflammation and improve survival by restoring beneficial gut bacteria that modulate immune responses and decrease toxic metabolite production. For hepatic encephalopathy, FMT addresses the overgrowth of ammonia-producing gut bacteria, lowering blood ammonia levels and improving cognitive function. Early trials report symptom reduction and improved quality of life, though larger studies are needed. FMT offers a novel, relatively safe intervention for patients with advanced liver disease who have limited treatment options, particularly when conventional therapies fail.
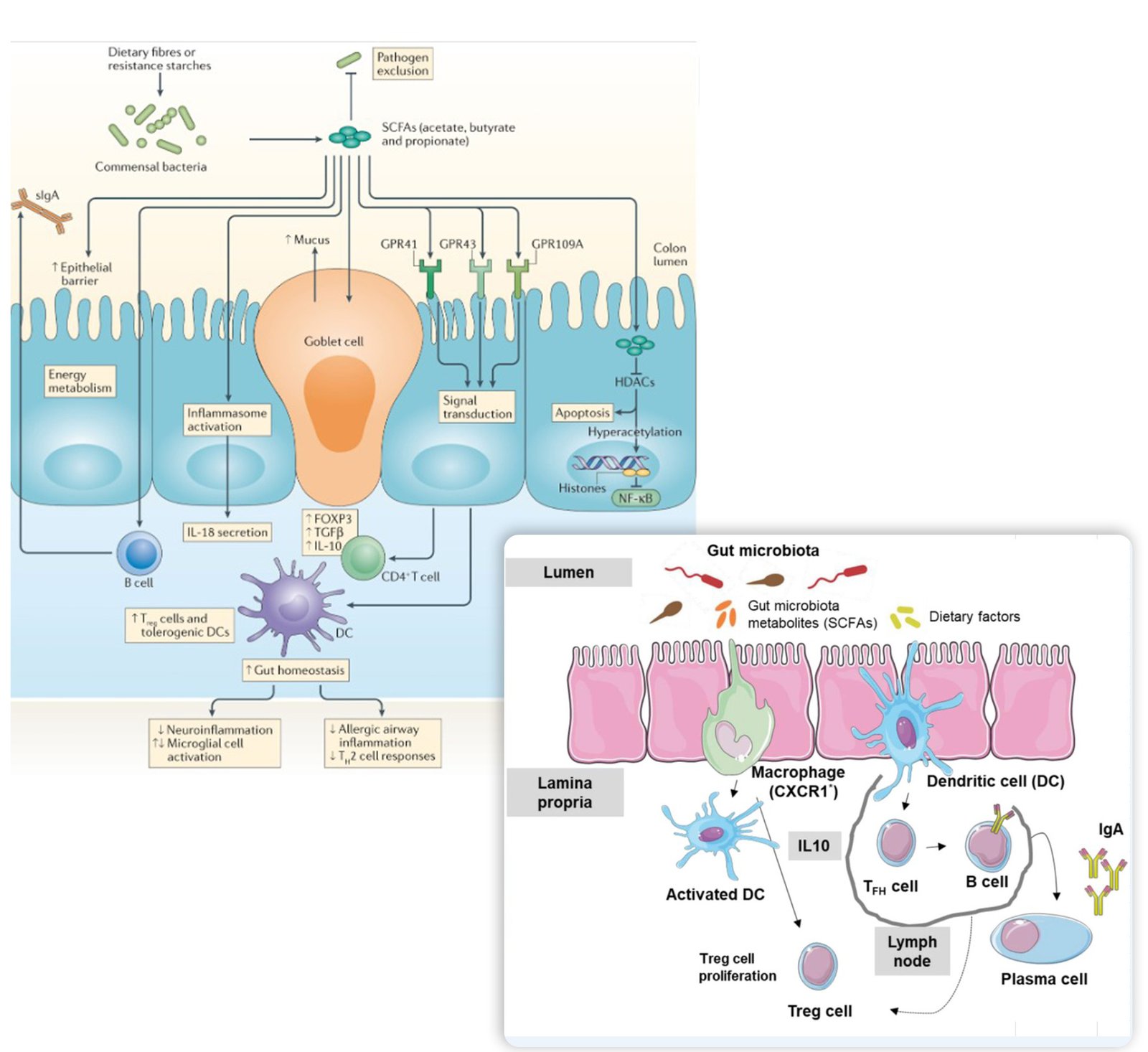
Metabolic-Immunologic-Systemic Disorders & FMT
FMT is being investigated for metabolic, immunologic, and systemic disorders through microbiota modulation. For obesity and metabolic syndrome, FMT may improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and alter energy harvest from food. In type 2 diabetes, it can enhance glucose metabolism and gut hormone secretion. For food allergies, FMT might promote immune tolerance by restoring gut barrier function and regulating immune responses. In chronic fatigue syndrome, it addresses gut dysbiosis linked to fatigue and inflammation. Excitingly, FMT has shown potential in enhancing immunotherapy responses in melanoma by modulating immune checkpoint activity via the microbiome. While most of these applications are in early research, they represent a promising frontier for conditions with limited treatment options.


Dr. Kenan Yüce
FMT Clinic
We Provide FMT Treatment For:
- ✅ Autism
- ✅ Clostridioides difficile Infection
- ✅ Alcoholic Hepatitis
- ✅ SIBO
- ✅ IBS
- ✅ Constipation
- ✅ Ulcerative Colitis
- ✅ Hepatic Encephalopathy
- ✅ Enhancing Immunotherapy Response (Melanoma)

Reviews on Google

FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Can you do it for this disease?
FMT has shown promise for various conditions, while its effectiveness can vary. We can perform it most of the time.
How many doses are needed?
Generally, one dose may be sufficient for gastrointestinal issues, but multiple doses might be necessary for other conditions.
How often do I have to have it done?
The frequency of treatments depends on the individual's condition, it may require 3-4 sessions per year or a single session. Usually, a single session. Please consult with our specialist for more information.
Do you ever recommend repeating a fecal microbiota transplant?
We might recommend repeating in 2 scenarios; First scenario is where it works for the patient and we have plenty room for improvement. This is usually for higher stages of various conditions. Second scenario is where patient is still willing to try the treatment so we change the donors and consider repeating the process.
What if it doesn't work for me?
Short answer: it may happen, there is no guarantee of recovering fully from every each disease. Results are varying case to case, yet we observe improved symptoms most of the time.
Am I a good candidate?
Usually, yes. FMT could be risky for people who are using immunosuppressant drugs, have had a recent bone marrow transplant, or have cirrhosis of the liver or advanced HIV or AIDS. If you fall into one of these groups, there might be the case where you are not a good candidate.
Do I need to be tested?
You are not required to be tested, we test donors. You are required to give your information and history instead.
I have a specific condition, can I get benefit from FMT?
While FMT has shown bright results for various conditions, we cannot guarantee it. However, since the risks are very low and potential reward is high, we are not against giving it a try.
Do you screen their sample for diseases?
Yes, donors undergo periodic blood and stool tests and answer a detailed questionnaire to ensure they meet the screening criteria for contributing to your health.
Are they from a single donor or multiple donors?
The stool is usually sourced from a single donor. We can use a mixture of donors for an additional fee, please consult with our specialist.
Can I see microbiome analysis of your donors?
While not routinely performed, microbiome analysis can be arranged upon specific request and for an additional cost. It will take around 40 days to complete. Please contact to our specialist to arrange one.
Can donor be a family member?
The clinic currently uses a pool of screened donors. In some cases, you can bring your own donor but clinic might not accept close family members as donors.
What do I need to do before the operation?
You will need to follow a 3-day liquid diet and use a laxative to cleanse and prepare your bowel.
Why do I need a liquid diet?
The liquid diet helps cleanse the bowel and prepares it for the transplant.
Can I follow the liquid diet in my country?
Yes, you can start the liquid diet in your home country.
How much does it cost?
Contact to our specialist with your preferences to get a free quote!
Is anesthesia used?
Anesthesia is used, but it is not general anesthesia. It is deep sedation-propofol. You will be in a deep sleep, you will not feel anything.
Do you administer pills or capsules?
No pills, no capsules. We use both endoscopy and colonoscopy to administer fresh stool.
What are the risks?
Potential risks of FMT include infection, temporary gastrointestinal discomfort, and allergic reactions which are significantly low. Long term risks are still to be known.
What does it include?
The treatments include fresh stool transplant, pre-treatment preparation (liquid diet and laxative), and post-treatment monitoring. No hidden costs, you will be shared with a custom treatment plan and prices depending on your preferences.
How can I receive the best results?
Adhering to the pre-treatment instructions, following a healthy lifestyle, improving sleep and maintaining regular communication with your healthcare provider can help optimize the results of FMT.
Can you travel afterwards, is it adviced to stay a few days?
You can leave the hospital on the same day.
How long can I expect to wait after FMT to receive results?
The effects of FMT can vary, but some patients may experience improvements within a few weeks.
How much time do we need to be in Istanbul?
Approximately 3 days.
